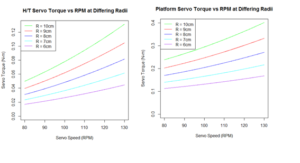
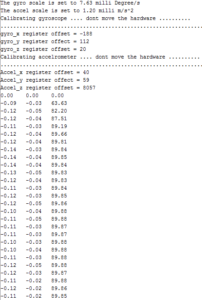
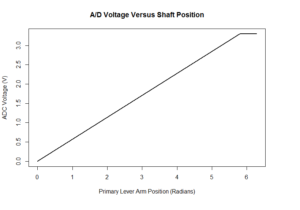
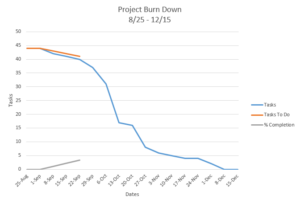
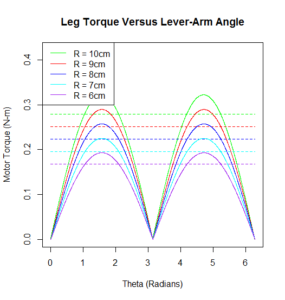
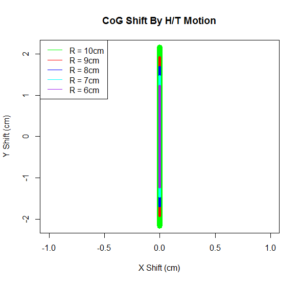
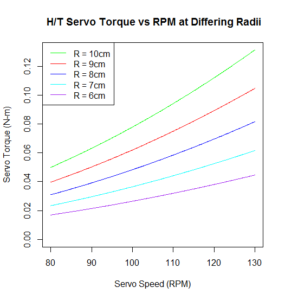
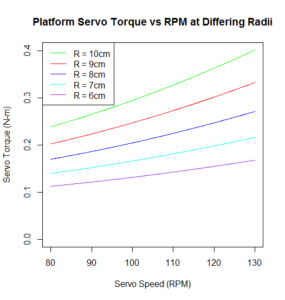
Telemetry and Custom Command Source Code
/*
* Telemetry and Custom Command Sample Arduino Code
* Telemetry Example: Monitor an extended I/O register value and send to control panel display
* Command Example: Add Robot unique MOVE, BLINK, and SERVO commands
*/
#include <Robot3DoTBoard.h> // instantiated as Robot3DoT at end of class header
#include <EEPROM.h>
#include <Wire.h> // I2C support
#include <Servo.h>
// IMU Variables
long HoldTime = micros();
#define MPU6050_AUX_VDDIO 0x01 // R/W
#define MPU6050_SMPLRT_DIV 0x19 // R/W
#define MPU6050_CONFIG 0x1A // R/W
#define MPU6050_GYRO_CONFIG 0x1B // R/W
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_CONFIG 0x1C // R/W
#define MPU6050_FF_THR 0x1D // R/W
#define MPU6050_FF_DUR 0x1E // R/W
#define MPU6050_MOT_THR 0x1F // R/W
#define MPU6050_MOT_DUR 0x20 // R/W
#define MPU6050_ZRMOT_THR 0x21 // R/W
#define MPU6050_ZRMOT_DUR 0x22 // R/W
#define MPU6050_FIFO_EN 0x23 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CTRL 0x24 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_ADDR 0x25 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_REG 0x26 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_CTRL 0x27 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_ADDR 0x28 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_REG 0x29 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_CTRL 0x2A // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_ADDR 0x2B // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_REG 0x2C // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_CTRL 0x2D // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_ADDR 0x2E // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_REG 0x2F // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_CTRL 0x30 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV4_ADDR 0x31 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV4_REG 0x32 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV4_DO 0x33 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV4_CTRL 0x34 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV4_DI 0x35 // R
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_STATUS 0x36 // R
#define MPU6050_INT_PIN_CFG 0x37 // R/W
#define MPU6050_INT_ENABLE 0x38 // R/W
#define MPU6050_INT_STATUS 0x3A // R
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_XOUT_H 0x3B // R
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_XOUT_L 0x3C // R
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_YOUT_H 0x3D // R
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_YOUT_L 0x3E // R
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_ZOUT_H 0x3F // R
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_ZOUT_L 0x40 // R
#define MPU6050_TEMP_OUT_H 0x41 // R
#define MPU6050_TEMP_OUT_L 0x42 // R
#define MPU6050_GYRO_XOUT_H 0x43 // R
#define MPU6050_GYRO_XOUT_L 0x44 // R
#define MPU6050_GYRO_YOUT_H 0x45 // R
#define MPU6050_GYRO_YOUT_L 0x46 // R
#define MPU6050_GYRO_ZOUT_H 0x47 // R
#define MPU6050_GYRO_ZOUT_L 0x48 // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_00 0x49 // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_01 0x4A // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_02 0x4B // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_03 0x4C // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_04 0x4D // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_05 0x4E // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_06 0x4F // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_07 0x50 // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_08 0x51 // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_09 0x52 // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_10 0x53 // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_11 0x54 // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_12 0x55 // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_13 0x56 // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_14 0x57 // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_15 0x58 // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_16 0x59 // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_17 0x5A // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_18 0x5B // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_19 0x5C // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_20 0x5D // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_21 0x5E // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_22 0x5F // R
#define MPU6050_EXT_SENS_DATA_23 0x60 // R
#define MPU6050_MOT_DETECT_STATUS 0x61 // R
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_DO 0x63 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_DO 0x64 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_DO 0x65 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_DO 0x66 // R/W
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_DELAY_CTRL 0x67 // R/W
#define MPU6050_SIGNAL_PATH_RESET 0x68 // R/W
#define MPU6050_MOT_DETECT_CTRL 0x69 // R/W
#define MPU6050_USER_CTRL 0x6A // R/W
#define MPU6050_PWR_MGMT_1 0x6B // R/W
#define MPU6050_PWR_MGMT_2 0x6C // R/W
#define MPU6050_FIFO_COUNTH 0x72 // R/W
#define MPU6050_FIFO_COUNTL 0x73 // R/W
#define MPU6050_FIFO_R_W 0x74 // R/W
#define MPU6050_WHO_AM_I 0x75 // R
// Defines for the bits, to be able to change
// between bit number and binary definition.
// By using the bit number, programming the sensor
// is like programming the AVR microcontroller.
// But instead of using “(1<<X)”, or “_BV(X)”,
// the Arduino “bit(X)” is used.
#define MPU6050_D0 0
#define MPU6050_D1 1
#define MPU6050_D2 2
#define MPU6050_D3 3
#define MPU6050_D4 4
#define MPU6050_D5 5
#define MPU6050_D6 6
#define MPU6050_D7 7
// AUX_VDDIO Register
#define MPU6050_AUX_VDDIO MPU6050_D7 // I2C high: 1=VDD, 0=VLOGIC
// CONFIG Register
// DLPF is Digital Low Pass Filter for both gyro and accelerometers.
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_DLPF_CFG0 MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_DLPF_CFG1 MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_DLPF_CFG2 MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET0 MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET1 MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET2 MPU6050_D5
// Combined definitions for the EXT_SYNC_SET values
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_0 (0)
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_1 (bit(MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET0))
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_2 (bit(MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET1))
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_3 (bit(MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET1)|bit(MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET0))
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_4 (bit(MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET2))
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_5 (bit(MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET2)|bit(MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET0))
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_6 (bit(MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET2)|bit(MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET1))
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_7 (bit(MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET2)|bit(MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET1)|bit(MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET0))
// Alternative names for the combined definitions.
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_DISABLED MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_0
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_TEMP_OUT_L MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_1
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_GYRO_XOUT_L MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_2
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_GYRO_YOUT_L MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_3
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_GYRO_ZOUT_L MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_4
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_ACCEL_XOUT_L MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_5
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_ACCEL_YOUT_L MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_6
#define MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_ACCEL_ZOUT_L MPU6050_EXT_SYNC_SET_7
// Combined definitions for the DLPF_CFG values
#define MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_0 (0)
#define MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_1 (bit(MPU6050_DLPF_CFG0))
#define MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_2 (bit(MPU6050_DLPF_CFG1))
#define MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_3 (bit(MPU6050_DLPF_CFG1)|bit(MPU6050_DLPF_CFG0))
#define MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_4 (bit(MPU6050_DLPF_CFG2))
#define MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_5 (bit(MPU6050_DLPF_CFG2)|bit(MPU6050_DLPF_CFG0))
#define MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_6 (bit(MPU6050_DLPF_CFG2)|bit(MPU6050_DLPF_CFG1))
#define MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_7 (bit(MPU6050_DLPF_CFG2)|bit(MPU6050_DLPF_CFG1)|bit(MPU6050_DLPF_CFG0))
// Alternative names for the combined definitions
// This name uses the bandwidth (Hz) for the accelometer,
// for the gyro the bandwidth is almost the same.
#define MPU6050_DLPF_260HZ MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_0
#define MPU6050_DLPF_184HZ MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_1
#define MPU6050_DLPF_94HZ MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_2
#define MPU6050_DLPF_44HZ MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_3
#define MPU6050_DLPF_21HZ MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_4
#define MPU6050_DLPF_10HZ MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_5
#define MPU6050_DLPF_5HZ MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_6
#define MPU6050_DLPF_RESERVED MPU6050_DLPF_CFG_7
// GYRO_CONFIG Register
// The XG_ST, YG_ST, ZG_ST are bits for selftest.
// The FS_SEL sets the range for the gyro.
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_FS_SEL0 MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_FS_SEL1 MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_ZG_ST MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_YG_ST MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_XG_ST MPU6050_D7
// Combined definitions for the FS_SEL values
#define MPU6050_FS_SEL_0 (0)
#define MPU6050_FS_SEL_1 (bit(MPU6050_FS_SEL0))
#define MPU6050_FS_SEL_2 (bit(MPU6050_FS_SEL1))
#define MPU6050_FS_SEL_3 (bit(MPU6050_FS_SEL1)|bit(MPU6050_FS_SEL0))
// Alternative names for the combined definitions
// The name uses the range in degrees per second.
#define MPU6050_FS_SEL_250 MPU6050_FS_SEL_0
#define MPU6050_FS_SEL_500 MPU6050_FS_SEL_1
#define MPU6050_FS_SEL_1000 MPU6050_FS_SEL_2
#define MPU6050_FS_SEL_2000 MPU6050_FS_SEL_3
// ACCEL_CONFIG Register
// The XA_ST, YA_ST, ZA_ST are bits for selftest.
// The AFS_SEL sets the range for the accelerometer.
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF0 MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF1 MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF2 MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_AFS_SEL0 MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_AFS_SEL1 MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_ZA_ST MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_YA_ST MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_XA_ST MPU6050_D7
// Combined definitions for the ACCEL_HPF values
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_0 (0)
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_1 (bit(MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF0))
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_2 (bit(MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF1))
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_3 (bit(MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF1)|bit(MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF0))
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_4 (bit(MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF2))
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_7 (bit(MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF2)|bit(MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF1)|bit(MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF0))
// Alternative names for the combined definitions
// The name uses the Cut-off frequency.
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_RESET MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_0
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_5HZ MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_1
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_2_5HZ MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_2
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_1_25HZ MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_3
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_0_63HZ MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_4
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_HOLD MPU6050_ACCEL_HPF_7
// Combined definitions for the AFS_SEL values
#define MPU6050_AFS_SEL_0 (0)
#define MPU6050_AFS_SEL_1 (bit(MPU6050_AFS_SEL0))
#define MPU6050_AFS_SEL_2 (bit(MPU6050_AFS_SEL1))
#define MPU6050_AFS_SEL_3 (bit(MPU6050_AFS_SEL1)|bit(MPU6050_AFS_SEL0))
// Alternative names for the combined definitions
// The name uses the full scale range for the accelerometer.
#define MPU6050_AFS_SEL_2G MPU6050_AFS_SEL_0
#define MPU6050_AFS_SEL_4G MPU6050_AFS_SEL_1
#define MPU6050_AFS_SEL_8G MPU6050_AFS_SEL_2
#define MPU6050_AFS_SEL_16G MPU6050_AFS_SEL_3
// FIFO_EN Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_SLV0_FIFO_EN MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_SLV1_FIFO_EN MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_SLV2_FIFO_EN MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_FIFO_EN MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_ZG_FIFO_EN MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_YG_FIFO_EN MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_XG_FIFO_EN MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_TEMP_FIFO_EN MPU6050_D7
// I2C_MST_CTRL Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK0 MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK1 MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK2 MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK3 MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_P_NSR MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_SLV_3_FIFO_EN MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_WAIT_FOR_ES MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_MULT_MST_EN MPU6050_D7
// Combined definitions for the I2C_MST_CLK
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_0 (0)
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_1 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK0))
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_2 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK1))
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_3 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK1)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK0))
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_4 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK2))
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_5 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK2)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK0))
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_6 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK2)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK1))
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_7 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK2)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK1)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK0))
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_8 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK3))
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_9 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK3)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK0))
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_10 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK3)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK1))
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_11 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK3)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK1)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK0))
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_12 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK3)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK2))
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_13 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK3)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK2)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK0))
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_14 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK3)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK2)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK1))
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_15 (bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK3)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK2)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK1)|bit(MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK0))
// Alternative names for the combined definitions
// The names uses I2C Master Clock Speed in kHz.
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_348KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_0
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_333KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_1
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_320KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_2
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_308KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_3
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_296KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_4
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_286KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_5
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_276KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_6
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_267KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_7
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_258KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_8
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_500KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_9
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_471KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_10
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_444KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_11
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_421KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_12
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_400KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_13
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_381KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_14
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_364KHZ MPU6050_I2C_MST_CLK_15
// I2C_SLV0_ADDR Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_RW MPU6050_D7
// I2C_SLV0_CTRL Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_LEN0 MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_LEN1 MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_LEN2 MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_LEN3 MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_GRP MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_REG_DIS MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_BYTE_SW MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_EN MPU6050_D7
// A mask for the length
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_LEN_MASK 0x0F
// I2C_SLV1_ADDR Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_RW MPU6050_D7
// I2C_SLV1_CTRL Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_LEN0 MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_LEN1 MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_LEN2 MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_LEN3 MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_GRP MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_REG_DIS MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_BYTE_SW MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_EN MPU6050_D7
// A mask for the length
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_LEN_MASK 0x0F
// I2C_SLV2_ADDR Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_RW MPU6050_D7
// I2C_SLV2_CTRL Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_LEN0 MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_LEN1 MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_LEN2 MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_LEN3 MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_GRP MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_REG_DIS MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_BYTE_SW MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_EN MPU6050_D7
// A mask for the length
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_LEN_MASK 0x0F
// I2C_SLV3_ADDR Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_RW MPU6050_D7
// I2C_SLV3_CTRL Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_LEN0 MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_LEN1 MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_LEN2 MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_LEN3 MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_GRP MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_REG_DIS MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_BYTE_SW MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_EN MPU6050_D7
// A mask for the length
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_LEN_MASK 0x0F
// I2C_SLV4_ADDR Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV4_RW MPU6050_D7
// I2C_SLV4_CTRL Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_DLY0 MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_DLY1 MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_DLY2 MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_DLY3 MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_DLY4 MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV4_REG_DIS MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV4_INT_EN MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV4_EN MPU6050_D7
// A mask for the delay
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_DLY_MASK 0x1F
// I2C_MST_STATUS Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_NACK MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_NACK MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_NACK MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_NACK MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV4_NACK MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_I2C_LOST_ARB MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV4_DONE MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_PASS_THROUGH MPU6050_D7
// I2C_PIN_CFG Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_CLKOUT_EN MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_I2C_BYPASS_EN MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_FSYNC_INT_EN MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_FSYNC_INT_LEVEL MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_INT_RD_CLEAR MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_LATCH_INT_EN MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_INT_OPEN MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_INT_LEVEL MPU6050_D7
// INT_ENABLE Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_DATA_RDY_EN MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_INT_EN MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_FIFO_OFLOW_EN MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_ZMOT_EN MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_MOT_EN MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_FF_EN MPU6050_D7
// INT_STATUS Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_DATA_RDY_INT MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_INT MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_FIFO_OFLOW_INT MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_ZMOT_INT MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_MOT_INT MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_FF_INT MPU6050_D7
// MOT_DETECT_STATUS Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_MOT_ZRMOT MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_MOT_ZPOS MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_MOT_ZNEG MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_MOT_YPOS MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_MOT_YNEG MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_MOT_XPOS MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_MOT_XNEG MPU6050_D7
// IC2_MST_DELAY_CTRL Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV0_DLY_EN MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV1_DLY_EN MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV2_DLY_EN MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV3_DLY_EN MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_I2C_SLV4_DLY_EN MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_DELAY_ES_SHADOW MPU6050_D7
// SIGNAL_PATH_RESET Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_TEMP_RESET MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_RESET MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_GYRO_RESET MPU6050_D2
// MOT_DETECT_CTRL Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_MOT_COUNT0 MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_MOT_COUNT1 MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_FF_COUNT0 MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_FF_COUNT1 MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY0 MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY1 MPU6050_D5
// Combined definitions for the MOT_COUNT
#define MPU6050_MOT_COUNT_0 (0)
#define MPU6050_MOT_COUNT_1 (bit(MPU6050_MOT_COUNT0))
#define MPU6050_MOT_COUNT_2 (bit(MPU6050_MOT_COUNT1))
#define MPU6050_MOT_COUNT_3 (bit(MPU6050_MOT_COUNT1)|bit(MPU6050_MOT_COUNT0))
// Alternative names for the combined definitions
#define MPU6050_MOT_COUNT_RESET MPU6050_MOT_COUNT_0
// Combined definitions for the FF_COUNT
#define MPU6050_FF_COUNT_0 (0)
#define MPU6050_FF_COUNT_1 (bit(MPU6050_FF_COUNT0))
#define MPU6050_FF_COUNT_2 (bit(MPU6050_FF_COUNT1))
#define MPU6050_FF_COUNT_3 (bit(MPU6050_FF_COUNT1)|bit(MPU6050_FF_COUNT0))
// Alternative names for the combined definitions
#define MPU6050_FF_COUNT_RESET MPU6050_FF_COUNT_0
// Combined definitions for the ACCEL_ON_DELAY
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY_0 (0)
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY_1 (bit(MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY0))
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY_2 (bit(MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY1))
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY_3 (bit(MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY1)|bit(MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY0))
// Alternative names for the ACCEL_ON_DELAY
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY_0MS MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY_0
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY_1MS MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY_1
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY_2MS MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY_2
#define MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY_3MS MPU6050_ACCEL_ON_DELAY_3
// USER_CTRL Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_SIG_COND_RESET MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_RESET MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_FIFO_RESET MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_I2C_IF_DIS MPU6050_D4 // must be 0 for MPU-6050
#define MPU6050_I2C_MST_EN MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_FIFO_EN MPU6050_D6
// PWR_MGMT_1 Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL0 MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL1 MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL2 MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_TEMP_DIS MPU6050_D3 // 1: disable temperature sensor
#define MPU6050_CYCLE MPU6050_D5 // 1: sample and sleep
#define MPU6050_SLEEP MPU6050_D6 // 1: sleep mode
#define MPU6050_DEVICE_RESET MPU6050_D7 // 1: reset to default values
// Combined definitions for the CLKSEL
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_0 (0)
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_1 (bit(MPU6050_CLKSEL0))
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_2 (bit(MPU6050_CLKSEL1))
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_3 (bit(MPU6050_CLKSEL1)|bit(MPU6050_CLKSEL0))
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_4 (bit(MPU6050_CLKSEL2))
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_5 (bit(MPU6050_CLKSEL2)|bit(MPU6050_CLKSEL0))
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_6 (bit(MPU6050_CLKSEL2)|bit(MPU6050_CLKSEL1))
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_7 (bit(MPU6050_CLKSEL2)|bit(MPU6050_CLKSEL1)|bit(MPU6050_CLKSEL0))
// Alternative names for the combined definitions
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_INTERNAL MPU6050_CLKSEL_0
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_X MPU6050_CLKSEL_1
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_Y MPU6050_CLKSEL_2
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_Z MPU6050_CLKSEL_3
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_EXT_32KHZ MPU6050_CLKSEL_4
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_EXT_19_2MHZ MPU6050_CLKSEL_5
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_RESERVED MPU6050_CLKSEL_6
#define MPU6050_CLKSEL_STOP MPU6050_CLKSEL_7
// PWR_MGMT_2 Register
// These are the names for the bits.
// Use these only with the bit() macro.
#define MPU6050_STBY_ZG MPU6050_D0
#define MPU6050_STBY_YG MPU6050_D1
#define MPU6050_STBY_XG MPU6050_D2
#define MPU6050_STBY_ZA MPU6050_D3
#define MPU6050_STBY_YA MPU6050_D4
#define MPU6050_STBY_XA MPU6050_D5
#define MPU6050_LP_WAKE_CTRL0 MPU6050_D6
#define MPU6050_LP_WAKE_CTRL1 MPU6050_D7
// Combined definitions for the LP_WAKE_CTRL
#define MPU6050_LP_WAKE_CTRL_0 (0)
#define MPU6050_LP_WAKE_CTRL_1 (bit(MPU6050_LP_WAKE_CTRL0))
#define MPU6050_LP_WAKE_CTRL_2 (bit(MPU6050_LP_WAKE_CTRL1))
#define MPU6050_LP_WAKE_CTRL_3 (bit(MPU6050_LP_WAKE_CTRL1)|bit(MPU6050_LP_WAKE_CTRL0))
// Alternative names for the combined definitions
// The names uses the Wake-up Frequency.
#define MPU6050_LP_WAKE_1_25HZ MPU6050_LP_WAKE_CTRL_0
#define MPU6050_LP_WAKE_2_5HZ MPU6050_LP_WAKE_CTRL_1
#define MPU6050_LP_WAKE_5HZ MPU6050_LP_WAKE_CTRL_2
#define MPU6050_LP_WAKE_10HZ MPU6050_LP_WAKE_CTRL_3
// Default I2C address for the MPU-6050 is 0x68.
// But only if the AD0 pin is low.
// Some sensor boards have AD0 high, and the
// I2C address thus becomes 0x69.
#define MPU6050_I2C_ADDRESS 0x68
// Declaring an union for the registers and the axis values.
// The byte order does not match the byte order of
// the compiler and AVR chip.
// The AVR chip (on the Arduino board) has the Low Byte
// at the lower address.
// But the MPU-6050 has a different order: High Byte at
// lower address, so that has to be corrected.
// The register part “reg” is only used internally,
// and are swapped in code.
typedef union accel_t_gyro_union
{
struct
{
uint8_t x_accel_h;
uint8_t x_accel_l;
uint8_t y_accel_h;
uint8_t y_accel_l;
uint8_t z_accel_h;
uint8_t z_accel_l;
uint8_t t_h;
uint8_t t_l;
uint8_t x_gyro_h;
uint8_t x_gyro_l;
uint8_t y_gyro_h;
uint8_t y_gyro_l;
uint8_t z_gyro_h;
uint8_t z_gyro_l;
} reg;
struct
{
int x_accel;
int y_accel;
int z_accel;
int temperature;
int x_gyro;
int y_gyro;
int z_gyro;
} value;
};
// Use the following global variables and access functions to help store the overall
// rotation angle of the sensor
unsigned long last_read_time;
float last_x_angle; // These are the filtered angles
float last_y_angle;
float last_z_angle;
float last_gyro_x_angle; // Store the gyro angles to compare drift
float last_gyro_y_angle;
float last_gyro_z_angle;
void set_last_read_angle_data(unsigned long time, float x, float y, float z, float x_gyro, float y_gyro, float z_gyro) {
last_read_time = time;
last_x_angle = x;
last_y_angle = y;
last_z_angle = z;
last_gyro_x_angle = x_gyro;
last_gyro_y_angle = y_gyro;
last_gyro_z_angle = z_gyro;
}
inline unsigned long get_last_time() {return last_read_time;}
inline float get_last_x_angle() {return last_x_angle;}
inline float get_last_y_angle() {return last_y_angle;}
inline float get_last_z_angle() {return last_z_angle;}
inline float get_last_gyro_x_angle() {return last_gyro_x_angle;}
inline float get_last_gyro_y_angle() {return last_gyro_y_angle;}
inline float get_last_gyro_z_angle() {return last_gyro_z_angle;}
// Use the following global variables and access functions
// to calibrate the acceleration sensor
float base_x_accel;
float base_y_accel;
float base_z_accel;
float base_x_gyro;
float base_y_gyro;
float base_z_gyro;
int read_gyro_accel_vals(uint8_t* accel_t_gyro_ptr) {
// Read the raw values.
// Read 14 bytes at once,
// containing acceleration, temperature and gyro.
// With the default settings of the MPU-6050,
// there is no filter enabled, and the values
// are not very stable. Returns the error value
accel_t_gyro_union* accel_t_gyro = (accel_t_gyro_union *) accel_t_gyro_ptr;
int error = MPU6050_read (MPU6050_ACCEL_XOUT_H, (uint8_t *) accel_t_gyro, sizeof(*accel_t_gyro));
// Swap all high and low bytes.
// After this, the registers values are swapped,
// so the structure name like x_accel_l does no
// longer contain the lower byte.
uint8_t swap;
#define SWAP(x,y) swap = x; x = y; y = swap
SWAP ((*accel_t_gyro).reg.x_accel_h, (*accel_t_gyro).reg.x_accel_l);
SWAP ((*accel_t_gyro).reg.y_accel_h, (*accel_t_gyro).reg.y_accel_l);
SWAP ((*accel_t_gyro).reg.z_accel_h, (*accel_t_gyro).reg.z_accel_l);
SWAP ((*accel_t_gyro).reg.t_h, (*accel_t_gyro).reg.t_l);
SWAP ((*accel_t_gyro).reg.x_gyro_h, (*accel_t_gyro).reg.x_gyro_l);
SWAP ((*accel_t_gyro).reg.y_gyro_h, (*accel_t_gyro).reg.y_gyro_l);
SWAP ((*accel_t_gyro).reg.z_gyro_h, (*accel_t_gyro).reg.z_gyro_l);
return error;
}
void calibrate_sensors() {
int num_readings = 10;
float x_accel = 0;
float y_accel = 0;
float z_accel = 0;
float x_gyro = 0;
float y_gyro = 0;
float z_gyro = 0;
accel_t_gyro_union accel_t_gyro;
//Serial.println(“Starting Calibration”);
// Discard the first set of values read from the IMU
read_gyro_accel_vals((uint8_t *) &accel_t_gyro);
// Read and average the raw values from the IMU
for (int i = 0; i < num_readings; i++) {
read_gyro_accel_vals((uint8_t *) &accel_t_gyro);
x_accel += accel_t_gyro.value.x_accel;
y_accel += accel_t_gyro.value.y_accel;
z_accel += accel_t_gyro.value.z_accel;
x_gyro += accel_t_gyro.value.x_gyro;
y_gyro += accel_t_gyro.value.y_gyro;
z_gyro += accel_t_gyro.value.z_gyro;
delay(100);
}
x_accel /= num_readings;
y_accel /= num_readings;
z_accel /= num_readings;
x_gyro /= num_readings;
y_gyro /= num_readings;
z_gyro /= num_readings;
// Store the raw calibration values globally
base_x_accel = x_accel;
base_y_accel = y_accel;
base_z_accel = z_accel;
base_x_gyro = x_gyro;
base_y_gyro = y_gyro;
base_z_gyro = z_gyro;
//Serial.println(“Finishing Calibration”);
}
// Motor Variables
int Motor1F = 5;
int Motor1R = 10;
int Motor1PWM = A9;
volatile int Motor1Speed = 0;
int Motor2F = 19;
int Motor2R = 20;
int Motor2PWM = 6;
volatile int Motor2Speed = 0;
volatile int Mot1State = 0;
volatile int Mot2State = 0;
// Servo Variables
//
Robot3DoTBoard Robot3DoT; // instantiated as Robot3DoT at end of class header
/*
* Command Example
* Step 1: Assign new command mnemonics ID numbers
* In our example we will be adding 3 custom commands (2 new and one predefined).
* The predefined MOVE command is intercepted and our robot unique code is to be
* run instead. The MOVE command mnemonic ID 0x01 is already defined in Configure.h
* The next two commands are new and assigned to the first two addresses in the
* custom command address space 0x40 – 0x5F.
*/
#define DYNSTAT 0x41
const uint8_t CMD_LIST_SIZE = 2; // we are adding 3 commands (MOVE, BLINK, SERVO)
/*
* Command Example
* Step 2: Register commands by linking IDs to their corresponding command handlers
* In our example when the MOVE command is intercepted the moveHandler is to be run.
* In a similar fashion the BLINK command calls the blinkHandler and SERVO the
* servoHandler.
*/
void moveHandler (uint8_t cmd, uint8_t param[], uint8_t n);
void dynstatHandler (uint8_t cmd, uint8_t param[], uint8_t n);
Robot3DoTBoard::cmdFunc_t onCommand[CMD_LIST_SIZE] = {{MOVE,moveHandler}, {DYNSTAT,dynstatHandler}};
/*
* Telemetry Example
* Step 1: Instantiate packet
* In our example we simulate a current sensor wired to MOTOR 2. MOTOR2_CURRENT_ID
* is defined as 0x02 in Configure.h
* To simulate the data stream coming from the sensor we will read ATmega32U4
* Register OCR4D which controls the duty cycle of MOTOR 2.
*/
Packet motorPWM(MOTOR2_CURRENT_ID); // initialize the packet properties to default values
void setup()
{
Serial.begin(9600); // default = 115200
Robot3DoT.begin();
// Initialize Motor To Off
pinMode(Motor1F, OUTPUT);
pinMode(Motor1R, OUTPUT);
pinMode(Motor1PWM, OUTPUT);
pinMode(Motor2F, OUTPUT);
pinMode(Motor2R, OUTPUT);
pinMode(Motor2PWM, OUTPUT);
digitalWrite(Motor1F,LOW);
digitalWrite(Motor1R,LOW);
digitalWrite(Motor2F,LOW);
digitalWrite(Motor2R,LOW);
// Initialize IMU
int error;
uint8_t c;
/*
Serial.println(F(“InvenSense MPU-6050”));
Serial.println(F(“June 2012”));
*/
// Initialize the ‘Wire’ class for the I2C-bus.
Wire.begin();
// default at power-up:
// Gyro at 250 degrees second
// Acceleration at 2g
// Clock source at internal 8MHz
// The device is in sleep mode.
//
error = MPU6050_read (MPU6050_WHO_AM_I, &c, 1);
/*
Serial.print(F(“WHO_AM_I : “));
Serial.print(c,HEX);
Serial.print(F(“, error = “));
Serial.println(error,DEC);
*/
// According to the datasheet, the ‘sleep’ bit
// should read a ‘1’. But I read a ‘0’.
// That bit has to be cleared, since the sensor
// is in sleep mode at power-up. Even if the
// bit reads ‘0’.
error = MPU6050_read (MPU6050_PWR_MGMT_2, &c, 1);
/*
Serial.print(F(“PWR_MGMT_2 : “));
Serial.print(c,HEX);
Serial.print(F(“, error = “));
Serial.println(error,DEC);
*/
// Clear the ‘sleep’ bit to start the sensor.
MPU6050_write_reg (MPU6050_PWR_MGMT_1, 0);
//Initialize the angles
calibrate_sensors();
set_last_read_angle_data(millis(), 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0);
/*
* Command Example
* Step 3: Tell 3DoT Robot software about new commands
*
*
*/
Robot3DoT.setOnCommand(onCommand, CMD_LIST_SIZE);
/* Telemetry Example
* Step 2: Modify default values assigned to internal properties as needed.
* Before a packet is created and sent, it is qualified. Specifically,
* the data in a packet must change by some amount from the previous
* packet and may not be sent with at a period less than some value.
* In most cases you can leave these values at their default values.
*/
delay(1000);
}
void loop()
{
Robot3DoT.loop();
// Set Motor State to the Telemetry Read Value
if (Mot1State == 1){ digitalWrite(Motor1F,HIGH);
digitalWrite(Motor1R,LOW);
} else if (Mot1State == 2) { digitalWrite(Motor1F,LOW);
digitalWrite(Motor1R,HIGH);
} else {digitalWrite(Motor1F,LOW);
digitalWrite(Motor1R,LOW);}
if (Mot2State == 1){ digitalWrite(Motor2F,HIGH);
digitalWrite(Motor2R,LOW);
} else if (Mot2State == 2) { digitalWrite(Motor2F,LOW);
digitalWrite(Motor2R,HIGH);
} else {digitalWrite(Motor2F,LOW);
digitalWrite(Motor2R,LOW);}
analogWrite(Motor1PWM, Motor1Speed);
analogWrite(Motor2PWM, Motor2Speed);
if (micros() – HoldTime > 500000){
HoldTime = micros();
Serial.write(“”);
Serial.write(Mot1State);
Serial.write(Motor1Speed);
Serial.write(Mot2State);
Serial.write(Motor2Speed);
Serial.write(“”);
}
// Read IMU Settings
//IMU();
// Set Servos to IMU Setting
}
/*
* Command Example
* Step 4: Write command handlers
*/
/*
* User Defined Command BLINK (0x40) Example
* A5 01 40 E4
*/
/*
* Override MOVE (0x01) Command Example
* A5 05 01 01 80 01 80 A1
*/
void moveHandler (uint8_t cmd, uint8_t param[], uint8_t n)
{
Mot1State = param[0];
Mot2State = param[2];
// Configure Inputs and Output
Motor1Speed = param[1];
Motor2Speed = param[3];
Serial.write(cmd); // move command = 0x01
Serial.write(n); // number of param = 4
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) // param = 01 80 01 80
{
Serial.write (param[i]);
}
} // moveHandler
/*
* User Defined Command SERVO (0x41) Example
* Rotate servo to 90 degrees
* A5 02 41 90 76
*/
void dynstatHandler (uint8_t cmd, uint8_t param[], uint8_t n)
{
Serial.write(cmd); // servo command = 0x41
Serial.write(n); // number of param = 1
for (int i=0;i<n;i++) // param = 90 degrees
{
Serial.write (param[i]);
}
} // servoHandler
// IMU LOOPS
void IMU()
{
int error;
double dT;
accel_t_gyro_union accel_t_gyro;
Serial.println(F(“”));
Serial.println(F(“MPU-6050”));
// Read the raw values.
cli();
error = read_gyro_accel_vals((uint8_t*) &accel_t_gyro);
sei();
// Get the time of reading for rotation computations
unsigned long t_now = millis();
Serial.print(F(“Read accel, temp and gyro, error = “));
Serial.println(error,DEC);
// Print the raw acceleration values
Serial.print(F(“accel x,y,z: “));
Serial.print(accel_t_gyro.value.x_accel, DEC);
Serial.print(F(“, “));
Serial.print(accel_t_gyro.value.y_accel, DEC);
Serial.print(F(“, “));
Serial.print(accel_t_gyro.value.z_accel, DEC);
Serial.println(F(“”));
// The temperature sensor is -40 to +85 degrees Celsius.
// It is a signed integer.
// According to the datasheet:
// 340 per degrees Celsius, -512 at 35 degrees.
// At 0 degrees: -512 – (340 * 35) = -12412
/*
Serial.print(F(“temperature: “));
dT = ( (double) accel_t_gyro.value.temperature + 12412.0) / 340.0;
Serial.print(dT, 3);
Serial.print(F(” degrees Celsius”));
Serial.println(F(“”));
// Print the raw gyro values.
Serial.print(F(“raw gyro x,y,z : “));
Serial.print(accel_t_gyro.value.x_gyro, DEC);
Serial.print(F(“, “));
Serial.print(accel_t_gyro.value.y_gyro, DEC);
Serial.print(F(“, “));
Serial.print(accel_t_gyro.value.z_gyro, DEC);
Serial.print(F(“, “));
Serial.println(F(“”));
*/
// Convert gyro values to degrees/sec
float FS_SEL = 131;
/*
float gyro_x = (accel_t_gyro.value.x_gyro – base_x_gyro)/FS_SEL;
float gyro_y = (accel_t_gyro.value.y_gyro – base_y_gyro)/FS_SEL;
float gyro_z = (accel_t_gyro.value.z_gyro – base_z_gyro)/FS_SEL;
*/
float gyro_x = (accel_t_gyro.value.x_gyro – base_x_gyro)/FS_SEL;
float gyro_y = (accel_t_gyro.value.y_gyro – base_y_gyro)/FS_SEL;
float gyro_z = (accel_t_gyro.value.z_gyro – base_z_gyro)/FS_SEL;
// Get raw acceleration values
//float G_CONVERT = 16384;
float accel_x = accel_t_gyro.value.x_accel;
float accel_y = accel_t_gyro.value.y_accel;
float accel_z = accel_t_gyro.value.z_accel;
// Get angle values from accelerometer
float RADIANS_TO_DEGREES = 180/3.14159;
// float accel_vector_length = sqrt(pow(accel_x,2) + pow(accel_y,2) + pow(accel_z,2));
float accel_angle_y = atan(-1*accel_x/sqrt(pow(accel_y,2) + pow(accel_z,2)))*RADIANS_TO_DEGREES;
float accel_angle_x = atan(accel_y/sqrt(pow(accel_x,2) + pow(accel_z,2)))*RADIANS_TO_DEGREES;
float accel_angle_z = 0;
// Compute the (filtered) gyro angles
float dt =(t_now – get_last_time())/1000.0;
float gyro_angle_x = gyro_x*dt + get_last_x_angle();
float gyro_angle_y = gyro_y*dt + get_last_y_angle();
float gyro_angle_z = gyro_z*dt + get_last_z_angle();
// Compute the drifting gyro angles
float unfiltered_gyro_angle_x = gyro_x*dt + get_last_gyro_x_angle();
float unfiltered_gyro_angle_y = gyro_y*dt + get_last_gyro_y_angle();
float unfiltered_gyro_angle_z = gyro_z*dt + get_last_gyro_z_angle();
// Apply the complementary filter to figure out the change in angle – choice of alpha is
// estimated now. Alpha depends on the sampling rate…
float alpha = 0.96;
float angle_x = alpha*gyro_angle_x + (1.0 – alpha)*accel_angle_x;
float angle_y = alpha*gyro_angle_y + (1.0 – alpha)*accel_angle_y;
float angle_z = gyro_angle_z; //Accelerometer doesn’t give z-angle
// Update the saved data with the latest values
cli();
set_last_read_angle_data(t_now, angle_x, angle_y, angle_z, unfiltered_gyro_angle_x, unfiltered_gyro_angle_y, unfiltered_gyro_angle_z);
sei();
// Send the data to the serial port
// Serial.print(F(“DEL:”)); //Delta T
// Serial.print(dt, DEC);
// Serial.print(F(“#ACC:”)); //Accelerometer angle
// Serial.print(accel_angle_x, 2);
// Serial.print(F(“,”));
// Serial.print(accel_angle_y, 2);
// Serial.print(F(“,”));
// Serial.print(accel_angle_z, 2);
// Serial.print(F(“#GYR:”));
// Serial.print(unfiltered_gyro_angle_x, 2); //Gyroscope angle
// Serial.print(F(“,”));
// Serial.print(unfiltered_gyro_angle_y, 2);
// Serial.print(F(“,”));
// Serial.print(unfiltered_gyro_angle_z, 2);
// Serial.print(F(“#FIL:”)); //Filtered angle
// Serial.print(angle_x, 2);
// Serial.print(F(“,”));
// Serial.print(angle_y, 2);
// Serial.print(F(“,”));
// Serial.print(angle_z, 2);
// Serial.println(F(“”));
}
// ——————————————————–
// MPU6050_read
//
// This is a common function to read multiple bytes
// from an I2C device.
//
// It uses the boolean parameter for Wire.endTransMission()
// to be able to hold or release the I2C-bus.
// This is implemented in Arduino 1.0.1.
//
// Only this function is used to read.
// There is no function for a single byte.
//
int MPU6050_read(int start, uint8_t *buffer, int size)
{
int i, n, error;
Wire.beginTransmission(MPU6050_I2C_ADDRESS);
n = Wire.write(start);
if (n != 1)
return (-10);
n = Wire.endTransmission(false); // hold the I2C-bus
if (n != 0)
return (n);
// Third parameter is true: relase I2C-bus after data is read.
Wire.requestFrom(MPU6050_I2C_ADDRESS, size, true);
i = 0;
while(Wire.available() && i<size)
{
buffer[i++]=Wire.read();
}
if ( i != size)
return (-11);
return (0); // return : no error
}
// ——————————————————–
// MPU6050_write
//
// This is a common function to write multiple bytes to an I2C device.
//
// If only a single register is written,
// use the function MPU_6050_write_reg().
//
// Parameters:
// start : Start address, use a define for the register
// pData : A pointer to the data to write.
// size : The number of bytes to write.
//
// If only a single register is written, a pointer
// to the data has to be used, and the size is
// a single byte:
// int data = 0; // the data to write
// MPU6050_write (MPU6050_PWR_MGMT_1, &c, 1);
//
int MPU6050_write(int start, const uint8_t *pData, int size)
{
int n, error;
Wire.beginTransmission(MPU6050_I2C_ADDRESS);
n = Wire.write(start); // write the start address
if (n != 1)
return (-20);
n = Wire.write(pData, size); // write data bytes
if (n != size)
return (-21);
error = Wire.endTransmission(true); // release the I2C-bus
if (error != 0)
return (error);
return (0); // return : no error
}
// ——————————————————–
// MPU6050_write_reg
//
// An extra function to write a single register.
// It is just a wrapper around the MPU_6050_write()
// function, and it is only a convenient function
// to make it easier to write a single register.
//
int MPU6050_write_reg(int reg, uint8_t data)
{
int error;
error = MPU6050_write(reg, &data, 1);
return (error);
} |